Biomechanical investigation of osseointegration of loosely and overtightly placed titanium implants
Abstract
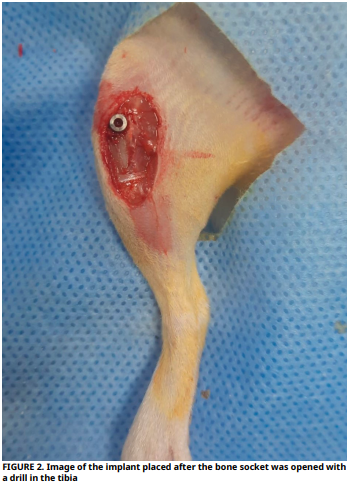
The objective of this research was to biomechanically assess the osseointegration of implants placed in bone sites prepared with diameters smaller than, larger than, or equal to the implant diameter. Twenty–one 6–month–old female Sprague Dawley rats weighing between 250–300 g were used in the study. The rats were divided into three groups and titanium implants, 2.5 mm diameter and 4 mm lenght, were placed in the cortico–cancellous bone structure in the metaphyseal parts of the right tibia bones of all rats included in the study. The study groups were; the group in which a bone bed of 2.2 mm in diameter and 4 mm in length was prepared and the implants were placed very tightly (n=7), the group in which a bone bed of 2.8 mm in diameter and 4 mm in length was prepared and the implants were placed loosely (n=7), and the control group in which a bone bed of 2.5 mm in diameter and 4 mm in length was prepared and the implants were placed. The rats were sacrificed 15 days after the operation. The implants were then subjected to torque analysis to measure biomechanical osseointegration values. Data were analyzed using One–Way Anova and Tukey HSD tests. Statistical significance was accepted as P<0.05. Biomechanical osseointegration values (N·cm-1) of overly tightly placed implants (12.86 ± 3.09) and implants in the control group (12.56 ± 3.58) were found to be significantly higher than those of loosely placed implants (6.56 ± 1.43) (P<0.05). Although the biomechanical osseointegration values of overly tightly placed implants those of implants in the control group were numerically higher, no statistically significant difference was found (P>0.05). As a result of the study, it was determined that tightly implant placement increased biomechanical osseointegration values. Additionally, osseointegration can be achieved without initial placement tightness too.
Downloads
References
Brånemark PI, Hansson BO, Adell R, Breine U, Lindström J, Hallén O, Ohman A. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Suppl. [Internet]. 1977 [cited Jun 25, 2025); 16:1-132. PMID: 356184. Available in: https://goo.su/rGHc
Carlsson L, Röstlund T, Albrektsson B, Albrektsson T, Brånemark PI. Osseointegration of titanium implants. Acta Orthop. [Internet]. 1986; 57(4):285-289. doi: https://doi.org/b75k27 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/17453678608994393
Bingul MB, Gul M, Dundar S, Bozoglan A, Kirtay M, Ozupek MF, Ozcan EC, Habek O, Tasdemir I. Effects of the application local zoledronic acid on different dental implants in rats on osseointegration. Drug. Des. Devel. Ther. [Internet]. 2024; 18:2249-2256. doi: https://doi.org/pmww DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S459125
Liu XN, Zhang Y, Li SB, Wang YY, Sun T, Li ZJ, Cai LZ, Wang XG, Zhou L, Lai RF. Study of a new bone–targeting titanium implant–bone interface. Int. J. Nanomed. [Internet]. 2016; 11:6307-6324. doi: https://doi.org/f9cn6k DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S119520
Emneus H, Stenram U, Baecklund J. An x–ray spectrographic investigation of the soft tissue around titanium and cobalt alloy implants. Acta Orthop.[Internet]. 1960; 30:226–236. doi: https://doi.org/fhcx9d DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/17453676109149543
Brånemark PI, Adell R, Breine U, Hansson BO, Lindström J, Ohlsson A. Intra–osseous anchorage of dental prostheses: I. Experimental studies. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. [Internet]. 1969; 3(2):81-100. doi: https://doi.org/drtkwh DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/02844316909036699
Alves–Rezende MCR, Capalbo LC, De Oliveira–Limírio JPJ, Capalbo BC, Limírio PHJO, Rosa JL. The role of TiO2 nanotube surface on osseointegration of titanium implants: Biomechanical and histological study in rats. Microsc. Res. Tech. [Internet]. 2020; 83(7):817-823. doi: https://doi.org/gp2429 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.23473
Overmann AL, Aparicio C, Richards JT, Mutreja I, Fischer NG, Wade SM, Potter BK, Davis TA, Bechtold JE, Forsberg JA, Dey D. Orthopaedic osseointegration: Implantology and future directions. J. Orthop. Res. [Internet]. 2020; 38(7):1445-1454. doi: https://doi.org/gscbx9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.24576
Al–Sabbagh M, Eldomiaty W, Khabbaz Y. Can osseointegration be achieved without primary stability? Dent. Clin. N. Am. [Internet]. 2019; 63(3):461-473. doi: https://doi.org/gpxjkd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2019.02.001
Acikan I, Dundar S. Biomechanical examination of osseointegration of titanium implants placed simultaneously with allogeneic bone transfer. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2022; 33(1):350-353. doi: https://doi.org/gp5nmd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000007880
Meredith N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int. J. Prosthodont. [Internet]. 1998 [cited Jun 25, 2025]; 11(5):491-501. PMID: 9922740. Available in: https://goo.su/uTIxc
Amor N, Geris L, Vander–Sloten J, Van Oosterwyck H. Modelling the early phases of bone regeneration around an endosseous oral implant. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. [Internet]. 2009; 12(4):459-468. doi: https://doi.org/cg3vsx DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10255840802687392
Osborn JS, Newesley H. Dynamic aspects of the implant–bone interface. In: Heimke G, editor. Dental Implants: Materials and systems. Munich (Germany): Carl Hanser Verlag; 1980. p. 111–123.
Sokmen N, Dundar S, Bozoglan A, Yildirim TT, Sokmen K, Sayeste E, Isayev A, Kirtay M. Effect of primary stabilisation on osseointegration of implants with local and systemic zoledronic acid application. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2022; 33(5):1276-1281. doi: https://doi.org/pmw2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000008236
Brunski JB. Biomechanical factors affecting the bone–dental implant interface. Clin. Mater. [Internet]. 1992; 10(3):153-201. doi: https://doi.org/fcct9f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0267-6605(92)90049-Y
Dundar S, Yaman F, Bozoglan A, Yildirim TT, Kirtay M, Ozupek MF, Artas G. Comparison of Osseointegration of Five Different Surfaced Titanium Implants. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2018; 29(7):1991-1995. doi: https://doi.org/pmw5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000004572
Al Subaie A, Emami E, Tamimi I, Laurenti M, Eimar H, Abdallah MN, Tamimi F. Systemic administration of omeprazole interferes with bone healing and implant osseointegration: an in vivo study on rat tibiae. J. Clin. Periodontol. [Internet]. 2016; 43(2):193-203. doi: https://doi.org/p7w2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12506
Dundar S, Bozoglan A, Bulmus O, Tekin S, Yildirim TT, Kirtay M, Toy VE, Gul M, Bozoglan MY. Effects of restraint stress and high–fat diet on osseointegration of titanium implants: an experimental study. Braz. Oral Res. [Internet]. 2020; 34:e008. doi: https://doi.org/n7q6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-3107bor-2020.vol34.0008
Eriksson AR, Albrektsson T. Temperature threshold levels for heat–induced bone tissue injury: a vital–microscopic study in the rabbit. J. Prosthet. Dent. [Internet]. 1983; 50(1):101-107. doi: https://doi.org/ds7tqm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3913(83)90174-9
De Santis E, Lang NP, Cesaretti G, Mainetti T, Beolchini M, Botticelli D. Healing outcomes at implants installed in sites augmented with particulate autologous bone and xenografts. An experimental study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implants Res. [Internet]. 2013; 24(1):77-86. doi: https://doi.org/f4h278 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02456.x
Albrektsson T, Johansson C. Osteoinduction, osteoconduction and osseointegration. Eur. Spine J. [Internet]. 2001; 10(Suppl. 2):S96-S101. doi: https://doi.org/bbh8n6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005860100282
Coelho PG, Marin C, Teixeira HS, Campos FE, Gomes JB, Guastaldi F, Anchieta RB, Silveira L, Bonfante EA. Biomechanical evaluation of undersized drilling on implant biomechanical stability at early implantation times. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2013; 71(2):E69-E75. doi: https://doi.org/f4n2gn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2012.10.008
Freitas AC Jr, Bonfante EA, Giro G, Janal MN, Coelho PG. The effect of implant design on insertion torque and immediate micromotion. Clin. Oral Implants Res. [Internet]. 2012; 23(1):113-118. doi: https://doi.org/fbns2d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02142.x
Gao X, Fraulob M, Haïat G. Biomechanical behaviours of the bone–implant interface: a review. J. R. Soc. Interface [Internet]. 2019; 16(156):20190259. doi: https://doi.org/gmkgrn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2019.0259
Duyck J, Roesems R, Cardoso MV, Ogawa T, De Villa–Camargos G, Vandamme K. Effect of insertion torque on titanium implant osseointegration: an animal experimental study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. [Internet]. 2015; 26(2):191-196. doi: https://doi.org/p7w3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12316
Gunes N, Gul M, Dundar S, Tekin S, Bozoglan A, Ozcan EC, Karasu N, Toy VE, Bingül MB. Biomechanical evaluation of implant osseointegration after guided bone regeneration with different bone grafts. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2021; 32(4):1545-1548. doi: https://doi.org/p7w5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000007102
Tekin S, Dundar S, Demirci F, Bozoglan A, Yildirim TT, Karaman T, Gul M. Biomechanical and biochemical analyses of the effects of propranolol on the osseointegration of implants. J. Craniofac. Surg. [Internet]. 2021; 32(3):1174-1176. doi: https://doi.org/p7w8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000006959