Evaluation of renal damage biomarkers in an experimental Pyelonephritis model ınduced by uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
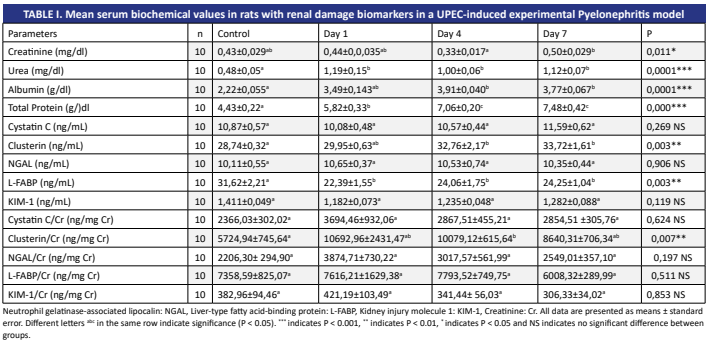
This study aims to determine the levels of biomarkers in rats on different days of the disease by creating a pyelonephritis model using Uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC). Forty rats were used in the study; 10 were designated as the control group and the remaining 30 rats were intrarenally administered UPEC to create a pyelonephritis model. Blood and urine samples were collected on days 1, 4 and 7 of the experiment. Histopathologically, it was determined that pyelonephritis occurred in all experimental groups. In serum samples, significant changes were observed in the groups’ clusterin, L-FABP and clusterin/Cr levels. In urine samples: while no significant changes were detected in Cr, clusterin, NGAL/Cr and clusterin/Cr levels, significant alterations were identified in NGAL, L-FABP, KIM-1, cystatin C, KIM-1/Cr, cystatin C/Cr and L-FABP/Cr levels. In the scope of the study, changes in the identified biomarkers in the serum and urine samples of rats with induced pyelonephritis were particularly evident. In evaluations conducted on different days of the disease, it was observed that urine NGAL, L-FABP, KIM-1 and cystatin C levels increased up to the 4th day compared to the control group. These findings suggest that urine biomarkers, in particular, may play a significant role in diagnosing pyelonephritis.
Downloads
References
Gupta K, Donnola SB, Sadeghi Z, Lu L, Erokwu BO, Kavran M, Hijaz A, Flask CA. Intrarenal Injection of Escherichia coli in a Rat Model of Pyelonephritis. J. Vis. Exp. [Internet]. 2017; 2017(125):e54649. doi: https://doi.org/ph5v DOI: https://doi.org/10.3791/54649-v
Ramakrishnan K, Scheid DC. Diagnosis and management of acute pyelonephritis in adults. Am. Fam. Physician. [Internet]. 2005 [cited Feb.26 2025]; 71(5):933-942. Available in: https://goo.su/lcGqP
Piccoli GB, Consiglio V, Deagostini MC, Serra M, BiolcatiM, Ragni F, Biglino A, De Pascale A, Frascisco MF, Veltri A, Porpiglia F. The clinical and imaging presentation of acute “non complicated” pyelonephritis: a new profile for an ancient disease. BMC Nephrol. [Internet]. 2011; 12:68. doi: https://doi.org/dx9nzz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-12-68
Sobel JD, Kaye D. Urinary Tract Infections. In: BennettJE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2015. p. 886-913. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4557-4801-3.00074-6
Whalan EJ. A Toxicologist’s Guide to Clinical Pathology inAnimals: Hematology, Clinical Chemistry; Urinalysis. 1st ed. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15853-2_1
Cooper KL, Badalato GM, Rutman MP. Infections of the rinary Tract. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, editors. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021. p.1129-1201.
Löfberg H, Grubb AO. Quantitation of gamma-trace in human biological fluids: indications for production in the central nervous system. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. [Internet]. 1979 ;39(7):619-626. doi: https://doi.org/cqx7rk DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/00365517909108866
Adingwupu OM, Barbosa ER, Palevsky PM, Vassalotti JA, Levey AS, Inker LA. Cystatin C as a GFR Estimation Marker in Acute and Chronic Illness: A Systematic Review. Kidney Med. [Internet]. 2023; 5(12):100727. doi: https://doi.org/ph6t DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100727
Munavalli V, Dhumale AJ, Kothiwale V A. Serum Cystatin C concentration levels as a marker of acute Kidney injury in critically ill Patients -A cross sectional study. APIK J. Int. Med. [Internet]. 2016; 4(3):9-14. doi: https://doi.rg/ph6v DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/2666-1802.258528
Satapathy S, Wilson MR. The Dual Roles of Clusterin in Extracellular and Intracellular Proteostasis. Trends Biochem. Sci. [Internet]. 2021; 46(8):652-660. doi: https://doi.org/gqj3rt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2021.01.005
Itakura E, Chiba M, Murata T, Matsuura A. Heparan sulfate is a clearance receptor for aberrant extracellular proteins. J. Cell Biol. [Internet]. 2020; 219(3):e201911126. doi: https://doi.org/ghswdt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201911126
Dieterle F, Perentes E, Cordier A, Roth DR, Verdes P, Grenet O, Pantano S, Moulin P, Wahl D, Mahl A, End P, Staedtler F, Legay F, Carl K, Laurie D, Chibout SD, Vonderscher J, Maurer G. Urinary clusterin, cystatin C, beta2-microglobulin and total protein as markers to detect drug-induced kidney injury. Nat. Biotechnol. [Internet]. 2010; 28(5):463-469. doi: https://doi.org/b6p92f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1622
Udupa V, Prakash V. Gentamicin induced acute renal damage and its evaluation using urinary biomarkers in rats. Toxicol. Rep. [Internet]. 2019;6:91-99. doi: https://doi.org/ph6x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.11.015
Crescenzi E, Leonardi A, Pacifico F. NGAL as a Potential Target in Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. [Internet]. 2021; 22(22):12333. doi: https://doi.org/gpw8wz DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212333
Defauw P, Schoeman JP, Leisewitz AL, Goddard A, Duchateau L, Aresu L, Meyer E, Daminet S. Evaluation of acute kidney injury in dogs with complicated or uncomplicated Babesia rossi infection. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. [Internet]. 2020; 11(3):101406. doi: https://doi.org/ph62 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2020.101406
Monari E, Troìa R, Magna L, Gruarin M, Grisetti C, Fernandez M, Balboni A, Giunti M, Dondi F. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin to diagnoseand characterize acute kidney injury in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. [Internet]. 2020; 34(1):176-185. doi: https://doi.org/ph63 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jvim.15645
Li B, Hao J, Zeng J, Sauter ER. SnapShot: FABP Functions. Cell. [Internet]. 2020; 182(4):1066-1066.e1. doi: https://doi.org/gp8k68 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.07.027
Xu Y, Xie Y, Shao X, Ni Z, Mou S. L-FABP: A novel biomarker of kidney disease. Clin. Chim. Acta. [Internet]. 2015; 445:85-90. doi: https://doi.org/f7c9kd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2015.03.017
Yokoyama T, Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Hoshino S, Yasuda T, Kimura K. Urinary excretion of liver type fatty acid binding protein accurately reflects the degree of tubulointerstitial damage. Am. J. Pathol. [Internet]. 2009; 174(6):2096-2106. doi: https://doi.org/bkrntq DOI: https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2009.080780
Kamijo-Ikemori A, Kimura K. Clinical utility of tubular markers in kidney disease: a narrative review. J. Lab. Precis. Med. [Internet]. 2022;7:27. doi: https://doi.org/ph64 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21037/jlpm-22-24
Medic B, Rovcanin B, Basta Jovanovic G, RadojevicŠkodric S, Prostran M. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Cardiovascular Diseases: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice. Biomed. Res. Int. [Internet]. 2015; 2015:854070. doi: https://doi.org/f84jnb DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/854070
Bland SK, Clark ME, Côté O, Bienzle D. A specific immunoassay for detection of feline kidney injury molecule 1. J. Feline Med. Surg. [Internet]. 2019; 21(12):1069-1079. doi: https://doi.org/gfns9x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1098612X18812494
Jiang Y, Xiong Z, Huang J, Yan F, Yao G, Lai B. Effective E. coli inactivation of core-shell ZnO@ZIF-8 photocatalysis under visible light synergize with peroxymonosulfate: Efficiency and mechanism. Chin. Chem. Lett. [Internet]. 2022; 33(1):415–423. doi: https://doi.org/ph65 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2021.06.058
Kasap B, Soylu A, Ertoy Baydar D, Kiray M, Tugyan K, Kavukçu S. Protective effects of bilirubin in an experimental rat model of pyelonephritis. Urology. [Internet]. 2012; 80(6):1389.e17-1389.e22. doi: https://doi.org/f2fj5j DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2012.07.029
Sabetkish N, Sabetkish S, Mohseni MJ, Kajbafzadeh AM. Prevention of Renal Scarring in Acute Pyelonephritis by Probiotic Therapy: an Experimental Study. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins. [Internet]. 2019; 11(1):158-164. doi: https://doi.org/ph66 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9363-x
Suckow MA, Danneman P, Brayton C. The Laboratory Mouse. Boca Raton, London, Newyork, Washington DC: CRC Press LLC; 2001. Available in: https://goo.su/Hgcq DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/9780849376276
Waynforth HB, Flecknell PA. Experimental and Surgical Technique In the Rat. 2nd ed. Amsterdam, Boston, Heidelberg, London, Newyork, Oxford, Paris, San Diego, Sanfrancisco, Singapore, Sydney, Tokyo: Academic Press; 1995. Available in: https://goo.su/vXYDhK8
Culling CFA, Allison RT, Barr WT. Cellular Pathology Technique. 4th ed. London; Boston: Butterworths. 1985. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-407-72903-2.50031-9
Poswiatowska-Kaszczyszyn I. Usefulness of serum cystatin C measurement for assessing renal function in cats. Bull Vet. Inst. Pulawy. [Internet]. 2012; 56(2):235–239. doi: https://doi.org/ph67 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/v10213-012-0042-0
Miyagawa Y, Takemura N, Hirose H. Evaluation of the measurement of serum cystatin C by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for humans as a marker of the glomerular filtration rate in dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. [Internet]. 2009; 71(9):1169-1176. doi: https://doi.org/ft65qf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.71.1169
Yan Y, Liu Y, Guo Y, Li B, Li Y, Wang X. Early diagnostic model of pyonephrosis with calculi based on radiomic features combined with clinical variables. Biomed. Eng. [Internet]. 2024; 23(1):97. doi: https://doi.org/ph69 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-024-01295-z
Zhang L, Li Y, Wang Z, Jiang J, Jin S, Zhu L, Lu Q, Chen J. The relationship between pathogenic bacteria distribution and the expression of serum YKL-40 and IL-8 in patients with acute pyelonephritis. Chin. J. Microecol. [Internet]. 2022; 34(10):1186-1190. doi: https://doi.org/ph7b
Yim HE, Yim H, Bae ES, Woo SU, Yoo KH. Predictive value of urinary and serum biomarkers in young children with febrile urinary tract infections. Pediatr. Nephrol. [Internet]. 2014; 29(11):2181-2189. doi: https://doi.org/f6jg2x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2845-0
Lezhenko HO, Zakharchenko NA. The role of nitric oxide synthase and cystatin C in the mechanisms of antimicrobial protection in children with urinary tract infections considering the etiological factor. Zaporozhye Med. J. [Internet]. 2022; 24(4):459-463. doi: https://doi.org/ph7c DOI: https://doi.org/10.14739/2310-1210.2022.4.255061
Islekel H, Soylu A, Altun Z, Yis U, Turkmen M, Kavukcu S. Serum and urine cystatin C levels in children with postpyelonephritic renal scarring: a pilot study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. [Internet]. 2007; 39(4):1241-1250. doi: https://doi.org/bc38t6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-007-9260-4
Sansanwal P, Li L, Sarwal MM. Inhibition of intracellular clusterin attenuates cell death in nephropathic cystinosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. [Internet]. 2015; 26(3):612-625. doi: https://doi.org/f64bqz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2013060577
Steblaj B, Kutter APN, Stirn M, Daminet S, Major A, Zini E. Endotoxic kidney injury in Beagle dogs assessed by serum creatinine and symmetric dimethylarginine, and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and clusterin. Res. Vet. Sci. [Internet]. 2023;162:104966. doi: https://doi.org/gs3q9x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2023.104966
Zhou X, Ma B, Lin Z, Qu Z, Huo Y, Wang J, Li B. Evaluation of the usefulness of novel biomarkers for drug-induced acute kidney injury in beagle dogs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2014; 280(1):30-35. doi: https://doi.org/f6h7z6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.07.002
Palm CA, Segev G, Cowgill LD, LeRoy BE, Kowalkowski KL, Kanakubo K, Westropp JL. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinaseassociated Lipocalin as a Marker for Identification of Acute Kidney Injury and Recovery in Dogs with Gentamicininduced Nephrotoxicity. J. Vet. Intern. Med. [Internet]. 2016; 30(1):200-205. doi: https://doi.org/ph7d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jvim.13819
Mizutani M, Hasegawa S, Matsushige T, Ohta N, Kittaka S, Hoshide M, Kusuda T, Takahashi K, Ichihara K, Ohga S. Distinctive inflammatory profile between acute focal bacterial nephritis and acute pyelonephritis in children. Cytokine. [Internet]. 2017; 99:24-29. doi: https://doi.org/ph7f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.06.012
Rafiei A, Abedi Arzefuni F, Mohammadjafari H, Yazdani-Charati J. The Urinary Level of Liver-type Fatty Acid Binding Protein in Children with Febrile UTI. Iran J. Kidney Dis. [Internet]. 2020 [cited Feb.26 2025]; 14(3):191-197. Available in: https://goo.su/P6qzNQ6
Ni AN, Shumatova TA, Sergeeva EV, Prikhodchenko NG, Zernova ES, Bykova OG. Endogenous Proteins in Infants and Toddlers with Urinary Tract Infections. Doctor Ru Magazine. [Internet]. 2021; 20(10):44–47. doi: https://doi.org/ph7g DOI: https://doi.org/10.31550/1727-2378-2021-20-10-44-47
Sergeeva EV, Nee A, Shumatova TA, Bykova OG, Prikhodchenko NG, Zernova ES. The role of increased intestinal permeability markers in developing urinary tract infection in children of the first three years of life. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. [Internet]. 2022; 12(2):339-346. https://doi.org/ph7h DOI: https://doi.org/10.15789/2220-7619-TRO-1799
Krzemien G, Turczyn A, Panczyk-Tomaszewska M, Kotula I, Demkow U, Szmigielska A. Prognostic value of serum and urine kidney injury molecule-1 in infants with urinary tract infection. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. [Internet]. 2019; 44(3):262-268. doi: https://doi.org/ph7j DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/ceji.2019.89600
Urbschat A, Obermüller N, Paulus P, Reissig M, Hadji P, Hofmann R, Geiger H, Gauer S. Upper and lower urinary tract infections can be detected early but not be discriminated by urinary NGAL in adults. Int. Urol. Nephrol. [Internet]. 2014; 46(12):2243-2249. doi: https://doi.org/f6sgv7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0831-x
Lee HE, Lee SH, Baek M, Choi H, Park K. Urinary Measurement of Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Injury Molecule-1 Helps Diagnose Acute Pyelonephritis in a Preclinical Model. J. Biomark. [Internet]. 2013; 2013:413853. doi: https://doi.org/gb6935 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/413853
Rius-Gordillo N, Ferré N, González JD, Ibars Z, Parada-Ricart E, Escribano J, DEXCAR Study Group. Role of dexamethasone in controlling the proinflammatory cytokine cascade in the first episode of paediatric acute pyelonephritis. Acta Paediatr. [Internet]. 2024; 113(3):564-572. doi: https://doi.org/ph7k DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.17034
Skowron B, Baranowska A, Dobrek L, Ciesielczyk K, Kaszuba-Zwoinska J, Wiecek G, Malska-Wozniak A, Strus M, Gil K. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, kidney injury molecule-1, uromodulin, and cystatin C concentrations in an experimental rat model of ascending acute kidney injury induced by pyelonephritis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2018; 69(4):625-637 doi: https://doi.org/ph7m
Anandkumar DG, Dheerendra PC, Vellakampadi D, Ramanathan G. Kidney injury molecule-1; is it a predictive marker for renal diseases? J. Nephropharmacol. [Internet]. 2023; 12(2):e10572. doi: https://doi.org/ph7n DOI: https://doi.org/10.34172/npj.2023.10572