Analysis of mineral and heavy metals in fish otoliths in theTigris River, Turkey
Abstract
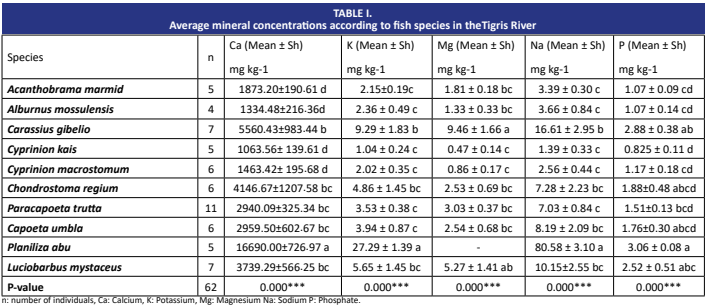
Rising pollution levels pose significant threats to fisheries. By analysing the different components of fish body structures, the interactions that occur in response to environmental changes can be better understood. Otoliths are structures in the inner ears of fish and record environmental changes that fish are exposed to throughout their lifes. Recent studies have shown that fish otoliths provide information on the accumulation of mineral and heavy metal in the environment. The accumulation of mineral and heavy metal in fish otoliths can be an important indicator for understanding environmental interactions and ultimately assessing the sustainability of fishery resources. In this study, 62 samples of Acanthobrama marmid, Alburnus mossulensis, Paracapoeta trutta, Capoeta umbla, Carassius gibelio, Chondrostoma regium, Cyprinion kais, Cyprinion macrostomum, Luciobarbus mystaceus and Planiliza abu were obtained from fishermen in the Tigris River. The presence of Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn were analysed by inductively couple plasma optical emission apectrometry (ICP-OES) in the otoliths. The average levels of heavy metals residues in the otoliths were determined as Co>Cr>Cu>Fe>Mn>Ni>Pb and Zn. The minerals Ca, K, Mg, Na and P were found to be statistically significant among fish species (P<0.05). According to Tukey HSD multiple comparison test, the highest values of Ca, K and Na were found in P. abu and Mg in C. gibelio. The data can be used as a reference for the evaluation of the accumulation of mineral and heavy metal in fish otoliths in terms of fishery management and environmental protection, and can be compared with the data from studies in different fisheries.
Downloads
References
Campana SE. Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: pathways, mechanisms and applications. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. [Internet]. 1999; 188:263-297. doi: https://doi.org/c2mc46 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps188263
Campana SE, Thorrold SR. Otoliths, increment and elements: keys to a comprehensive understanding of fish populations? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. [Internet]. 2001; 58(1):30–38. doi: https://doi.org/cs4ckn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/f00-177
Phelps QE, Edwards KR, Willis DW. Precision of five structures for estimating age of common carp. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. [Internet]. 2007; 27(1): 103-105. doi: https://doi.org/cdfgj9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1577/M06-045.1
Jawad L, Mahé K. Fluctuating asymmetry in asteriscii otoliths of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) collected from three localities in Iraqi rivers linked to environmental factors. Fishes. [Internet]. 2022; 7(2):91. doi: https://doi.org/n96q DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7020091
Tanabe T, Kayama S, Ogura M, Tanaka S. Daily increment formation in otoliths of juvenile skipjack tuna Katsuwonus pelamis. Fish. Sci. [Internet]. 2003; 69(4):731-737. doi: https://doi.org/b3vkbc DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1444-2906.2003.00680.x
Morales-Nin B, Panfili J. Seasonality in the deep sea and tropics revisited: what can otoliths tell us? Mar. Freshw. Res. [Internet]. 2005; 56(5):585-598. doi: https://doi.org/cdrvgk DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/MF04150
Gao YW. Stable isotope analyses in otoliths of cod (Gadus morhua L., 1758): implication for long-term environmental changes in the Canadian Atlantic. Hamilton: McMaster University, 1997; p. 96. Available in: https://goo.su/B9030R
Ren D, Yonghua G, Qingling F. Enrichment of Pb, Hg and Cr in cultured carp otolith. Afr. J. Biotechnol. [Internet]. 2012; 11(8):1939-1947. doi: https://doi.org/n96r DOI: https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.3108
Kalish JM. Otolith microchemistry: Validation of the effects of physiology, age and environment on otolith composition. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. [internet]. 1989; 132(3):151-178. doi: https://doi.org/bjsq5s DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(89)90126-3
Fowler AJ, Campana SE, Thorrold SR, Jones CM. Experimental assessment of the effect of temperature and salinity on elemental composition of otoliths using laser ablation ICPMS. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. [Internet]. 1995; 52(7):1431-1441. doi: https://doi.org/cwwjnh DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/f95-138
Bath GE, Thorrold SR, Jones CM, Campana SE, Mclaren JM, Lam JWH. Strontium and barium uptake in aragonitic otoliths of marine fish. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2000; 64(10):1705-1714. doi: https://doi.org/c28c5p DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00419-6
Kraus RT, Secor DH. Incorporation of strontium into otoliths of an estuarine fish. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. [Internet]. 2004; 302(1):85-106. doi: https://doi.org/dbxzsp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2003.10.004
Thresher RE. Elemental composition of otoliths as a stock delineator in fishes. Fish. Res. [Internet]. 1999; 43(13):165-204. doi: https://doi.org/d763f2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-7836(99)00072-7
Degens ET, Deuser WG, Haedrich RL. Molecular structure and composition of fish otoliths. Mar. Biol. [Internet]. 1969 [cited Jul. 22 2024]; 2:105-113. Available in: https://goo.su/U7XA6l DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347005
Mugiya Y, Hakomori T; Hatsutori K. Trace metal incorporation into otoliths and scales in the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Comp. Toxicol. [Internet]. 1991; 99(3):327-331. doi: https://doi.org/d2mhrt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0742-8413(91)90250-W
Pannela G. Fish otoliths: daily growth layer and periodical patterns. Science [Internet]. 1971; 173(4002):1124–1127. doi: https://doi.org/dz22zx DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.173.4002.1124
Ranaldi MM, Gagnon MM. Trace metal incorporation in otoliths of pink snapper (Pagrus auratus) as an environmental monitor. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2010; 152(3):248–255. doi: https://doi.org/fmthmm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.04.012
Secor DH, Ohta T, Nakayama K, Tanaka M. Use of otolith microanalysis to determine estuarine migrations of Japanese sea bass Lateolabrax japonicus distributed in Ariake Sea. Fish. Sci. [Internet]. 1998; 64(5):740–743. doi: https://doi.org/n96t DOI: https://doi.org/10.2331/fishsci.64.740
Limburg KE. Otolith strontium traces environmental history of subyearling American shad Alosa sapidissima. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. [Internet]. 1995 [cited Jul. 19 2024]; 119(1-3):25–35. Available in: https://goo.su/16Hk9Fj DOI: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps119025
Sadovy Y, Severin KP. Trace elements in biogenic aragonite: correlation of body growth rate and strontium levels in the otoliths of the white grunt, Haemulon plumier (Pisces: Haemulidae). Bull. Mar. Sci. 1992; 50:237-257. Available in: https://goo.su/VkFkdyx
Gillanders BM, Kingsford MJ. Spatial variation in elemental composition of otoliths of three species of fish (family Sparidae). Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. [Internet]. 2003; 57(5-6):1049–1064. doi: https://doi.org/b8x6n4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7714(03)00009-X
Pontual H, Bertignac M, Battaglia A, Bavouzet G, Moguedet P; Groison AL. A pilot tagging experiment on European hake (Merluccius merluccius): methodology and preliminary results. ICES J. Mar. Sci. [Internet]. 2003; 60(6):1318–1327. doi: https://doi.org/fs46hs DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1054-3139(03)00149-8
Elsdon TS, Gillanders BM. Interactive effects of temperature and salinity on otolith chemistry: challenges for determining environmental histories of fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci: 2002; 59(11):1796–1808. doi: https://doi.org/cfh5kp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/f02-154
Swearer SE, Forrester GE, Steele MA, Brooks AJ, Lea DW. Spatio-temporal and interspecific variation in otolith trace-elemental fingerprints in a temperate estuarine fish assemblage. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. [Internet]. 2003;56(5-6):1111–1123. doi: https://doi.org/c2w9b4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00317-7
Martin GB, Thorrold SR. Temperature and salinity effectson magnesium, manganese, and barium incorporation in otoliths of larval and early juvenile spot Leiostomus xanthurus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. [Internet]. 2005; 293:223–232. doi: https://doi.org/bzvd7c DOI: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps293223
Vasconcelos RP, Reis-Santos P, Tanner S, Fonseca V, Latkoczy C, Günther D, Costa MJ, Cabral H. Discriminating estuarine nurseries for five fish species through otolith elemental fingerprints. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. [Internet]. 2007; 350:117–126. doi: https://doi.org/frnrv6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07109
Reis Santos P, Vasconcelos R, Ruano M, Latkoczy C, Günther D, Costa MJ, Cabral H. Interspecific variation of otolith chemistry in estuarine fish nurseries. J. Fish Biol. [Internet]. 2008; 72(10):2595–2614. doi: https://doi.org/c792cf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2008.01871.x
Thorrold SR, Jones CM, Campana SE. Response of otolith microchemistry to environmental variations experienced by larval and juvenile Atlantic croaker (Micropogonius undulatus). Limnol. Oceanogr. [Internet]. 1997; 42(1):102–111. doi: https://doi.org/frnnsm DOI: https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1997.42.1.0102
Rooker JR, Secor DH, DeMetrio G, Schloesser R, Block BA, Neilson J.D. Natal homing and connectivity in Atlantic bluefin tuna populations. Sci. [Internet]. 2008; 322(5902):742–744. doi: https://doi.org/c966md DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1161473
Moreau G, Barbeau C, Frenette JJ, Saint-Onge J, Simoneau M. Zinc, manganese, and strontium in opercula and scales of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) as indicators of lake acidification. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. [Internet]. 1983; 40(10):1685-1691. doi: https://doi.org/cj694q DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/f83-195
Gauldie R W, Fournier DA, Dunlop DE, Coote G. Atomic emission and proton microprobe studies of the ion con- tent of otoliths of chinook salmon aimed at recovering the temperature life history of individuals. Comp. Bio- chem. Physiol. A, Physiol. [Internet]. 1986; 84(4):507-515. doi: https://doi.org/b8vxr9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9629(86)90374-9
Evans DW, Dodoo DK and Hanson DJ. Trace elements con- centrations in fish livers: Implications of variations with fish size in pollution monitoring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. [Inter- net]. 1993; 26(6):329–334. doi: https://doi.org/bzdr3x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(93)90576-6
Rashed MN. Monitoring of environmental heavy metals in fish from Nasser Lake. Environ. Int. [Internet]. 2001; 27(1):27–33. doi: https://doi.org/fwnrjd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(01)00050-2
Papagiannis I, Kagalou I, Leonardos J, Petridis D, Kalfakak- ou V. Copper and zinc in four freshwater fish species from Lake Pamvotis (Greece), Environm. Int. [Internet]. 2004; 30(3):357–362. doi: https://doi.org/dvq4pz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2003.08.002
Guhathakurta H, Kaviraj A. Heavy metal concentration in water, sediment, shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and mul- let (Liza parsia) in some brackish water ponds of Sun- derban, India. 2000. Mar. Pollut. Bull. [Internet]. 2000; 40(11):914-920. doi: https://doi.org/b9tmgh DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00028-X
Kargin F. Metal concentrations in tissues of the fresh- water fish Capoeta barroisi from the Seyhan River (Tur- key). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. [Internet]. 1998; 60(5):822–828. doi: https://doi.org/crmct4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001289900701
Canli M, Atli G. The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Medi- terranean fish species. Environ. Pollut. [Internet]. 2003; 121(1):129–136. doi: https://doi.org/c6vkwh DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00194-X
Fernandes C, Fontaínhas-Fernandes A, Peixoto F, Salga- do MA. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in Liza saliens from the Esmoriz-Paramos coastal lagoon, Portugal. Ec- otoxicol. Environ. Saf. [Internet]. 2007; 66(3):426–431. doi: https://doi.org/cs99z5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.02.007
Karadede-Akin H, Ünlü E. Heavy metal concentrations in water, sediment, fish and some benthic organisms from Tigris River, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. [Internet]. 2007; 131:323-337. doi: https://doi.org/bkcvvx DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9478-0
Herrera-Reveles AT, Lemus M, Marín B, Prin JL. Trace metal incorporation in otoliths of a territorial coral reef fish (Abudefduf saxatilis) as an environmental monitor- ing tool. In: E3S Web of Conferences. Proceedings of the 16th Intrenational Conference on Heavy Metals in the Environment. EDP Sci. J. [Internet]. 2013; 1:34007. doi: https://doi.org/n983 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20130134007
Sturgeon RE. Current practice and recent developments in analytical methodology for trace metal analysis of soils, plants and water. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. [Internet]. 2000; 31(11-14):1479-1512. doi: https://doi.org/b2sf35 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620009370522
IBM Corp. Released. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 23.0. Armonk: IBM Corp.2021 [cited Jul 22 2024] Available in: https://n9.cl/rc9b9
Sümbüloğlu K, Sümbüloğlu V. Biyoistatistik. hatipoğlu basım ve yayım san. Tic. Ltd. Şti. Ankara, 2002.
Gao Y, Feng Q, Ren D, Qiao L, Li S. The relationship be- tween trace elements in fish otolith of wild carp and hydrochemical conditions. Fish Physiol. Biochem. [Inter- net]. 2010; 36(1):91-100. doi: https://doi.org/b3wkr6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-008-9294-2
Fengqin D, Shengrong L, Lina Y, Wenjie L, Jing L, Wen- yan S. Relationship of phosphorus content in carp oto- liths with that in ambient water in Xiaoxi Port of the Tai- hu Lake, East China. Afr. J. Biotechnol. [Internet]. 2011; 10(54):11206-11213. doi: https://doi.org/n987 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.1932
Milton DA, Tenakanai CD, Chenery SR. Can the move- ments of barramundi in the Fly River region, Papua New Guinea be traced in their otoliths?. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. [Internet]. 2000; 50(6):855–868. doi: https://doi.org/ bpgq2m DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.2000.0608
Tong SL, Ho CY, Pang FY. Monitoring of Ba, Mn, Cu and Ni during estuarine mixing. Anal. Sci. [Internet]. 1997; 13(Supplement):373-378. doi: https://doi.org/c4nnkm DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.13.Supplement_373
Elsdon TS, Gillanders BM. Temporal variability in stron- tium, calcium, barium, and manganese in estuaries: im- plications for reconstructing environmental histories of fish from chemicals in calcified structures. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. [Internet]. 2006; 66(1-2):147-156. doi: https://doi.org/bdg7nj DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.08.004