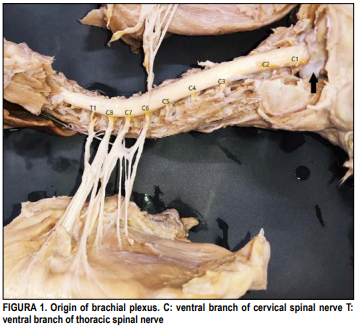
Macroanatomical study on origin and distribution of Caucasian Lynx (Lynx lynx dinniki)’s the brachial plexus
Abstract
This study aimed to determine the formation of the plexus brachialis, the nerves that ramify from the plexus, and their last branches in the Caucasian Lynx. It was found that the formation of the brachial plexus contributed to the ventral branches of the C6th, C7th, C8th, and T1th spinal nerves in the lynx. The ventral root of the C6th spinal nerve gave rise to the suprascapular nerve, the ventral of the C6th and C7th spinal nerve to the subscapular nerves and musculocutaneous nerve, the C7th to the cranial pectoral nerve, the C8th to the caudal pectoral nerve, the C8th and T1th to the lateral pectoral nerve, the radial nerve and the ulnar nerve, and the C7th, C8th, and T1th to the median nerve. The network formed by these branches was the origin of the cranial, caudal, long and lateral pectoral nerves, the suprascapular nerve to the extrinsic muscles of the scapula, the subscapular nerve to the intrinsic muscle of the scapula, the axillary nerve to the major teres and caudal portion of the subscapular muscle, the musculocutaneous nerve to the biceps muscle and its cutaneous, the radial nerve to the muscles of the forearm and pawn craniolateral aspect, the median nerve to the flexor digitorium superficial and profound muscles, and the ulnar nerve to the flexor ulnar carpi and the flexor deep digitorium muscle.
Downloads
References
Hansen K. Bobcat: master of survival. First Edition. Oxford University Press: 2007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780195183030.001.0001
Dyce KM, Sack WO, Wensing CJG, Textbook of veterinary natomy-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences: 2009.
König HE, Liebich HG. Veterinary anatomy of domesticanimals: Textbook and colour atlas. 2020.
Nur IH, Keles H, Pérez W. Origin and distribution of thebrachial plexus of the Van cats. Anat. Histol. Embryol. Internet].2020;49(2):251-259. doi: https://doi.org/n6ns DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/ahe.12523
Souza-Junior PC, Wronski JG, Carvalho ND, Abidu-Figueiredo M. Brachial Plexus in the Leopardus geoffroyi. Ciênc. Anim. Brasil. [Internet]. 2018;19:e51240. doi: https://doi.org/n6nv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v19e-51240
De Lahunta A, Glass EN, Kent M. De Lahunta’s veterinary neuroanatomy and clinical neurology. Elsevier HealthSciences: 2020.
Aubert L, Carozzo C, Devillaire AC, Crevier-Denoix N, Moissonnier P. Macro-and microanatomical characterization of the cat brachial plexus. Cells TissuesOrgans [Internet]. 2004;176(4):205-210. doi: https://doi.org/fwb65q DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000077037
Meachen-Samuels J, Van Valkenburgh B. Forelimbindicators of prey-size preference in the Felidae. J. Morphol[Internet]. 2009;270(6):729-744. doi: https://doi.org/djpzkd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jmor.10712
Nzalak JO, Eki MM, Sulaiman MH, Umosen AD, Salami SO, Maidawa SM, Ibe CS. Gross anatomical studies of the bones of the thoracic limbs of the Lion (Panthera leo). J. Vet. Anat [Internet]. 2010; 3(2):65-71. doi: https://doi.org/n6nw DOI: https://doi.org/10.21608/jva.2010.44901
Ari HH, Yurdakul I, Aksoy G. A macroscopic study on themuscles and tendons of forepaws in the anatolian bobcat(Lynx lynx). Slov. Vet. Res [Internet]. 2019; 56(4). doi: https://doi.org/n6nx DOI: https://doi.org/10.26873/SVR-702-2019
Veterinaria NA. International committee on veterinary gross anatomical nomenclature (ICVGAN). Hannover: Published by the Editorial Committee; 2017.
Aslan K. The comparative macroanatomic investigationon the brachial plexus of the native cat (Felis domestica) and White New Zealand Rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Istanbul Univ Vet Fak Derg [Internet].1994; 20:197-208.
ATecirlioglu S. Komparatif Veteriner Anatomi Sinir Sistemi. Ankara: A.U¨. Vet. Fak. Yay. 389. A.U¨. Basimevi. 1983.
Ansón A, Gil F, Laredo FG, Soler M, Belda E, Ayala MD, Agut A. Correlative ultrasound anatomy of the felinebrachial plexus and major nerves of the thoracic limb. Vet Radiol Ultrasound [Internet]. 2013;54(2):185-193. doi: https://doi.org/f4r2nb DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/vru.12012
Ghoshal NG, Magilton JH. The brachial plexus (plexusbrachialis) of the cat (Felis domesticus). Anat. Histol. Embryol. [Internet]. 1972;1(1):6-13. doi: https://doi.org/df8db4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0264.1972.tb00947.x
Demiraslan Y, Aykut M, Özgel Ö. Macroanatomicalcharacteristics of plexus brachialis and its branches inmartens (Martes foina). Turk J Vet Anim Sci [Internet]. 2015; 39(6):693-698. doi: https://doi.org/n6nz DOI: https://doi.org/10.3906/vet-1506-48
Mencalha R, Fernandes N, do Santo-Sousa CA, Abidu-Figueiredo M. A cadaveric study to determine the mínimum volume of methylene blue to completely color the nerves of brachial plexus in cats. An update in forelimb and shoulder surgeries. Acta Cir. Bras [Internet]. 2014; 29(6):382-388. doi: https://doi.org/n6n2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-86502014000600006