Transformación Afín Bidimensional (AT2D) para Interpolación de Velocidades Geodésicas utilizando Soluciones Semanales SIRGAS-CON
Resumen
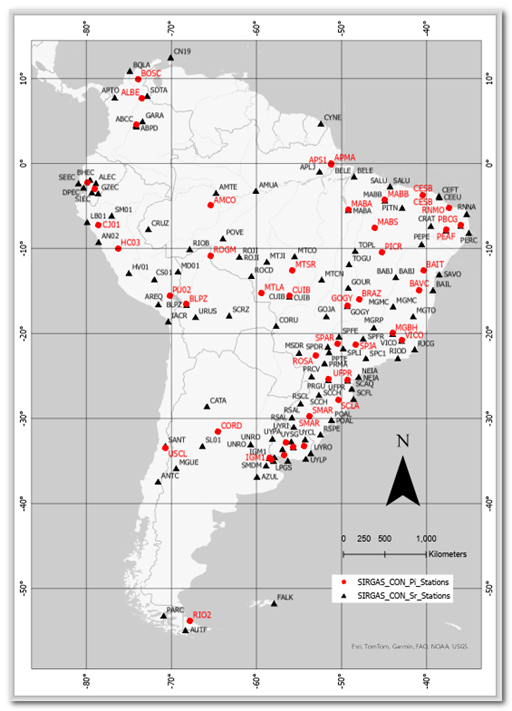
Los modelos de velocidades geodésicas son cruciales para la transformación de coordenadas de una época de referencia a una época de observación. Su desarrollo suele requerir mucho tiempo y actualizaciones frecuentes para mantener su validez. Para abordar el problema de su validez, este estudio examina el uso de la Transformación Afín Bidimensional (AT2D) para interpolar velocidades en estaciones GNSS en Sudamérica. La AT2D se basa en una triangulación desde estaciones SIRGAS-CON circundantes, con velocidades conocidas, durante un intervalo de tiempo específico. Las velocidades resultantes del método AT2D y de los modelos VEMOS, sobre cincuenta estaciones, se compararon contra sus velocidades conocidas, lo que permitió el cálculo de residuos para la evaluación de la calidad. En el 82% de las comparaciones, la AT2D exhibió un RMSE menor (±1,4 mm/año) que los modelos VEMOS (±3,6 mm/año). Los resultados muestran que el método AT2D reproduce eficazmente las velocidades SIRGAS-CON cuando las estaciones se ubican en la misma placa tectónica. La AT2D ofrece una flexibilidad temporal que permite realizar ajustes ante saltos abruptos o discontinuidades en los datos GNSS. Además, la AT2D resulta eficiente y precisa para calcular velocidades actualizadas en contextos locales o regionales relevantes para la topografía y la ingeniería geodésica.
Descargas
Citas
Bevis, M., Brown, A. (2014). Trajectory models and reference frames for crustal motion geodesy. Journal of Geodesy. Volume 88, pages 283–311. doi: 10.1007/s00190-013-0685-5.
Drewes, H., Heidbach, O. (2005). Deformation of the South American crust estimated from finite element and collocation methods', in Sansò, F. (ed.). A Window on the Future of Geodesy. IAG Symposia, vol. 128, pp. 544–549. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27432-4_92.
Drewes, H. (2020). Modelar el movimiento de la superficie terrestre. Velocidades continuas y coordenadas por etapas. Technische Universität München (TUM), International Association of Geodesy (IAG), Sistema de Referencia Geodésico para las Americas (SIRGAS). Webinar SIRGAS, 28 August 2020. Available at: www.sirgas.ipgh.org/docs/Boletines/2020_Drewes_Webinar_VEMOS.pdf.
Drewes, H., Sánchez, L. (2020). Velocity model for SIRGAS 2017: VEMOS2017. PANGAEA. Technische Universität München, Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM), IGS RNAAC SIRGAS. [Online]. doi: 10.1594/PANGAEA.912350.
Drewes, H., Seitz, M., Sánchez, L. (2024). Realisation of the Non-Rotating Terrestrial Reference Frame by an Actual Plate Kinematic and Crustal Deformation Model (APKIM2020). International Association of Geodesy Symposia. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/1345_2024_276.
Feder, J. (1988). The Perimeter-Area Relation. Fractals: Physics of Solids and Liquids. Springer, Boston, MA. doi:10.1007/978-1-4899-2124-6_12.
Ghilani, C. (2018). Adjustment Computations: Spatial Data Analysis. 6th edn. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Hoboken, New Jersey.
Gómez, D., Piñón, D., Smalley, R., Bevis, M., Cimbaro, S., Lenzano, L., Barón, J. (2016). Reference frame access under the effects of great earthquakes: a least squares collocation approach for non-secular post-seismic evolution. Journal of Geodesy, Volume 90, Issue 3, pp. 263-273. DOI:10.1007/s00190-015-0871-8.
Harris, C., Millman, K., van der Walt, S., Gommers, R., Virtanen, P., Cournapeau, D., Wieser, E., Taylor, J., Berg, S., Smith, N., Kern, R., Picus, M., Hoyer, S., Kerkwijk, M., Brett, M., Haldane, A., Fernández del Río, J., Wiebe, M., Peterson, P., Oliphant, T. (2020). Array programming with NumPy. Nature 585(7825), pp. 357–362. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2649-2.
Hoyer, M., Arciniegas, S., Pereira, K., Fagard, H., Maturana, R., Torchetti, R., Drewes, H., Kumar, M., Seeber, G. (1998). The Definition and Realization of the Reference System in the SIRGAS Project', in Brunner, F.K. (ed.). Advances in Positioning and Reference Frames. International Association of Geodesy Symposia, vol. 118. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Lay, D., Lay, S., McDonald, J. (2016). Linear Algebra and Its Applications. 5th edn. Pearson.
Li, Z., Zhu, C., Gold, C., Wu, H., Fritsch, D. (2005). Digital Terrain Modeling: Principles and Methodology. CRC Press.
Sánchez, L. (2023). SIRGAS Regional Network Associate Analysis Centre, Technical Report 2022. IGS Technical Report 2022. doi:10.48350/179297.
Sánchez, L. Drewes, H. (2020). Geodetic monitoring of the variable surface deformation in Latin America. International Association of Geodesy Symposia Series, vol. 152. Springer, Cham. doi: 10.1007/1345_2020_91
Sánchez, L., Drewes, H., Kehm, A., Seitz, M. (2022). SIRGAS reference frame analysis at DGFI-TUM. Journal of Geodetic Science, 12(1), pp. 92–119. doi:0.1515/jogs-2022-0138.
SIRGAS Analysis Centre at DGFI-TUM. (2024a). SIRGAS continuously operating network. Available at: www.sirgas.org/en/sirgas-realizations/sirgas-con-network/.
SIRGAS Analysis Centre at DGFI-TUM. (2024b). SIRGAS continuously operating stations. Available at: www.sirgas.org/en/stations/station-list/.
SIRGAS Analysis Centre at DGFI-TUM. (2024c). VEMOS: Velocity model for SIRGAS. Available at: www.sirgas.org/en/velocity-model/.
Suárez, H. (2023). SIGGMA GEODETIC CALCULATOR – SGC. Sociedad de Ingenieros Geodestas, Geomáticos y Agrimensores de Venezuela – SIGGMA. Available at: www.siggma.xyz/sgc/.
Suárez, H., Arenas, I., Cano, N., Marcano, P., Diaz, M., Martínez, A. (2024). Local TIN Interpolation (LTI) for the calculation of horizontal velocity components, based on weekly time series from SIRGAS-CON stations. Sistema de Referencia Geodésico para las Américas (SIRGAS). Simposio SIRGAS 2024, Bogotá, Colombia, 18-21 de noviembre de 2024.
Yan, Y., Li, M., Dai, L., Guo, J., Dai, H., Tang, W. (2022). Construction of “Space-Sky-Ground” Integrated Collaborative Monitoring Framework for Surface Deformation in Mining Area. Remote Sensing, 14, 840. doi: 10.3390/rs14040840.
Derechos de autor 2025 Hermógenes David Suárez Acosta, Ileanis del Carmen Arenas Bermúdez, Nilbeny Nibraska Cano Finol, Paola Chiquinquirá Marcano Márquez, Alisleidy Paola Martínez Martínez

Esta obra está bajo licencia internacional Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
Copyright
La Revista Técnica de la Facultad de Ingeniería declara que los derechos de autor de los trabajos originales publicados, corresponden y son propiedad intelectual de sus autores. Los autores preservan sus derechos de autoría y publicación sin restricciones, según la licencia pública internacional no comercial ShareAlike 4.0










_2.04__.27_p__._m__.__.png)